Stores a precompiled statement in the data dictionary for execution later.
Usage
Embedded, Interactive, Module, ODBC, JDBC
Description
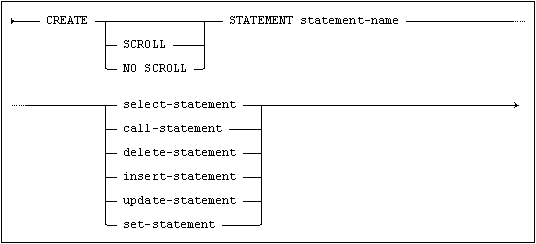
The statement specified, stored with the name statement-name, is compiled and optimized and thereafter stored in its compiled form in the data dictionary.
The statement can then be executed through the EXECUTE STATEMENT command (see EXECUTE STATEMENT.) A statement that produces a result set (e.g. SELECT), needs a cursor to read it.
You can use the SCROLL option to specify that the result set should be read by a scrollable cursor.
If you use the NO SCROLL option, the result set will only be accessible for no-scroll cursors.
If you do not specify an option, the result set can be used by both scroll and no-scroll cursors.
Once the precompiled statement has been created, only cursors with the correct scroll mode can be used to read the result set.
Language Elements
call-statement, see CALL.
delete-statement, see DELETE.
insert-statement, see INSERT.
select-statement, see SELECT.
set-statement, see SET.
update-statement, see UPDATE.
Restrictions
The ident executing the CREATE STATEMENT command must have adequate access rights to perform the stored command.
Notes
The statement-name must not be the same as any other statement name in the schema.
Parameter marker references may be used in the statement to denote values that are supplied when the statement is executed. Parameter markers can either be a ? or on the form :variable.
Examples
CREATE SCROLL STATEMENT seltaba
SELECT col1, col2
FROM taba WHERE col3 < 10
CREATE STATEMENT updtaba
UPDATE taba SET col2 = :inpvar
WHERE col3 < :col3var
CREATE STATEMENT callme
CALL proc1('ABC', ?)
Standard Compliance
|
Standard |
Compliance |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Mimer SQL extension |
The CREATE STATEMENT command is a Mimer SQL extension. |