Defines action to be taken for errors and exception conditions.
Usage
Embedded.
Description
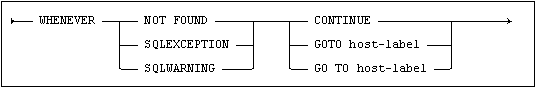
The action taken in the event of a condition arising during execution of an SQL statement is governed by the most recently issued WHENEVER statement. There are three different types of conditions: NOT FOUND, SQLEXCEPTION and SQLWARNING. See Return Status and Conditions for a description of the different condition types.
The action taken is as follows:
•CONTINUE
Program execution continues at the next sequential statement of the source program.
•GOTO
Program execution continues at the source code statement identified by host-label, where host-label is a program label in a program written according to the host language.
Notes
If a condition in an SQL statement is not covered by an explicit WHENEVER statement issued earlier in the host program code, CONTINUE will be assumed.
It’s recommended to set SQLEXCEPTION to CONTINUE action first of all in the diagnostics part of the code, to avoid the risk of a looping application.
Example
...
GOTO 1025
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLEXCEPTION GOTO 1600
1025 CONTINUE
EXEC SQL DELETE FROM MYTABLE
...
1060 CONTINUE
EXEC SQL WHENEVER SQLEXCEPTION CONTINUE
EXEC SQL GET DIAGNOSTICS ...
Standard Compliance
|
Standard |
Compliance |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
SQL-2016 |
Core |
Fully compliant. |