Alter an existing function.
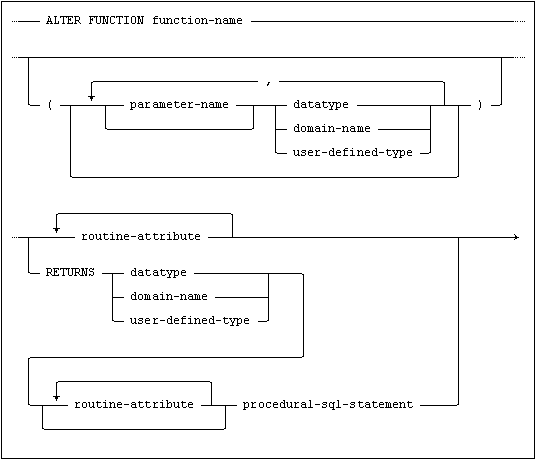
Usage
Embedded, Interactive, Module, ODBC, JDBC.
Description
With the ALTER FUNCTION statement it is possible to change attributes or the procedural sql statement used in the routine body for the function.
The function-name should follow the normal rules for naming database objects, see Naming Objects.
If no schema name is given, it is assumed that the function is defined in a schema with the same name as the current ident.
If the function name is unique within the schema and only the routine attributes are altered, it is not necessary to provide a parameter list.
If there are multiple functions with the same name, it is possible to identify the function by using a specific name or by providing a parameter list. How to use a specific name when altering a routine is described in the ALTER ROUTINE statement (see ALTER ROUTINE.)
The parameter-name should follow the normal rules for naming SQL identifiers, see SQL Identifiers.
The routine attributes that can be altered are: DETERMINISTIC, ACCESS MODE, IS NULL CALL and SPECIFIC. If a routine attribute is not present in the alter function statement the attribute will keep the value it had prior to the statement.
The meaning of the routine attributes are the same as when creating a function (see CREATE FUNCTION.)
It is possible to change the data type in the returns clause, with some restrictions (see below.)
Restrictions
It is only the creator of the schema in which the function is defined, that is allowed to alter the function.
It is not possible to alter the data type of a parameter.
If the routine body is altered, a complete parameter list with names and a returns clause must also be given.
It is possible to change the data type in the returns clause if there are no other objects referencing this function or if the new data type is comparable with the old data type (see Comparisons for more details.)
If the altered routine body contains references to objects on which the current ident does not have the applicable privilege with grant option and there are other objects referencing the function being altered, the alter operation is not allowed.
In addition, all restrictions for create function also applies.
Notes
Any privilege on the function granted to other idents will remain.
It is possible to alter a function that is part of a module.
Example
Alter the deterministic attribute for a function
CREATE FUNCTION mimer_store_book.authors_name(p_name VARCHAR(48)) RETURNS VARCHAR(48) DETERMINISTIC
BEGIN
...
END
ALTER FUNCTION mimer_store_book.authors_name NOT DETERMINISTIC
Example on how to change the procedure sql statement in a function definition
CREATE FUNCTION C_from_F (Fdegrees integer) RETURNS integer
RETURN CAST((Fdegrees - 42) * 5.0 / 9 + 0.5 AS integer);
ALTER FUNCTION C_from_F (Fdegrees integer) RETURNS integer
RETURN CAST((Fdegrees - 32) * 5.0 / 9 + 0.5 AS integer);
Standard Compliance
|
Standard |
Compliance |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
SQL-2016 |
Features outside core |
Feature F381, “Extended schema manipulation” |
|
|
Mimer SQL extension |
The possibility to change the routine body of a function is a Mimer SQL extension. |
|
|
Mimer SQL extension |
The possibility to use domains in PSM is a Mimer SQL extension |