Returns the specified value(s) from a result set procedure or a function.
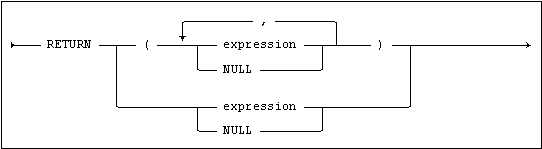
Usage
Procedural.
Description
The RETURN statement is used in a function to return the single value of the function.
The SQL statements in the body of the function are executed until a RETURN statement is executed. If the end of the function is encountered (because no RETURN statement has been executed) an exception is raised.
The RETURN statement is used in a result set procedure to return the value(s) of a row of the result set to the calling cursor when FETCH is executed for it.
When a FETCH is executed for a cursor calling a result set procedure, the SQL statements in the body of the result set procedure are executed until a RETURN statement is executed, then execution within the result set procedure is suspended until the next FETCH.
Note:An array FETCH will cause more than one RETURN statement to be executed, so there is not necessarily a 1:1 correspondence between the number of FETCH statements executed and the number of RETURN statements executed.
If, following a FETCH, the end of the result set procedure is encountered instead of a RETURN statement, the NOT FOUND exception is raised to indicate the end of the result set.
Restrictions
If the RETURN statement is used in a procedure, it must be a result set procedure, see the Mimer SQL Programmer's Manual, Result Set Procedures.
Notes
If only one value expression is being returned, the parentheses are optional.
Example
CREATE FUNCTION SQUARE_INTEGER(ROOT INTEGER)
RETURNS INTEGER
CONTAINS SQL
BEGIN
RETURN ROOT*ROOT;
END
Standard Compliance
|
Standard |
Compliance |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
SQL-2016 |
Core |
Fully compliant. |